Paper Review: "Pregel: A System for Large-Scale Graph Processing"
2021-10-02A technical review of Google's Pregel paper, explaining its vertex-centric approach to distributed graph processing, how its superstep synchronization model simplifies parallel computing, and why it became foundational for modern graph processing frameworks.
In this article, I will introduce the following paper on Pregel, a distributed graph processing engine developed by Google:
Pregel: A System for Large-Scale Graph Processing - Malewicz et al. (Google) 2010
About Pregel
Graph compute engines that process graph-structured datasets can be broadly classified into two types:
- Graph processing engines designed to run on a single machine (e.g., Cassovary)
- Graph processing engines designed to run on a distributed architecture (e.g., Apache Giraph, Project Pegasus)
Pregel belongs to the latter category and is a distributed graph processing engine developed within Google.
Pregel features a message-passing-based architecture that distributes Supersteps across worker machines for execution. It follows a vertex-centric approach, where each vertex maintains flags indicating whether processing is complete, current values, message queues, and other relevant data.
The system employs a master-worker architecture. The master manages the state of all workers, partitions graph data for load balancing, and ensures scalability and fault tolerance across distributed machines.
The paper discusses Pregel's architecture, its C++ API, and its performance characteristics.
Supersteps
Supersteps are units of execution applied to each vertex.
For example, the following slide illustrates how each vertex is updated at each Superstep:
(Slide Example: "Propagating the highest value in the graph")
During this process, the Compute() function is abstracted in the Pregel API, allowing for various algorithms beyond simple maximum value propagation.
For instance, the PageRank algorithm can be implemented in Pregel as follows:
class PageRankVertex : public Vertex<double, void, double> {
public:
virtual void Compute(MessageIterator* msgs) {
if (superstep() >= 1) {
double sum = 0;
for (; !msgs->Done(); msgs->Next())
sum += msgs->Value();
*MutableValue() = 0.15 / NumVertices() + 0.85 * sum;
}
if (superstep() < 30) {
const int64 n = GetOutEdgeIterator().size();
SendMessageToAllNeighbors(GetValue() / n);
} else {
VoteToHalt();
}
}
};
Master and Worker Architecture
The cluster-wide architecture using a master and worker configuration is structured as follows:
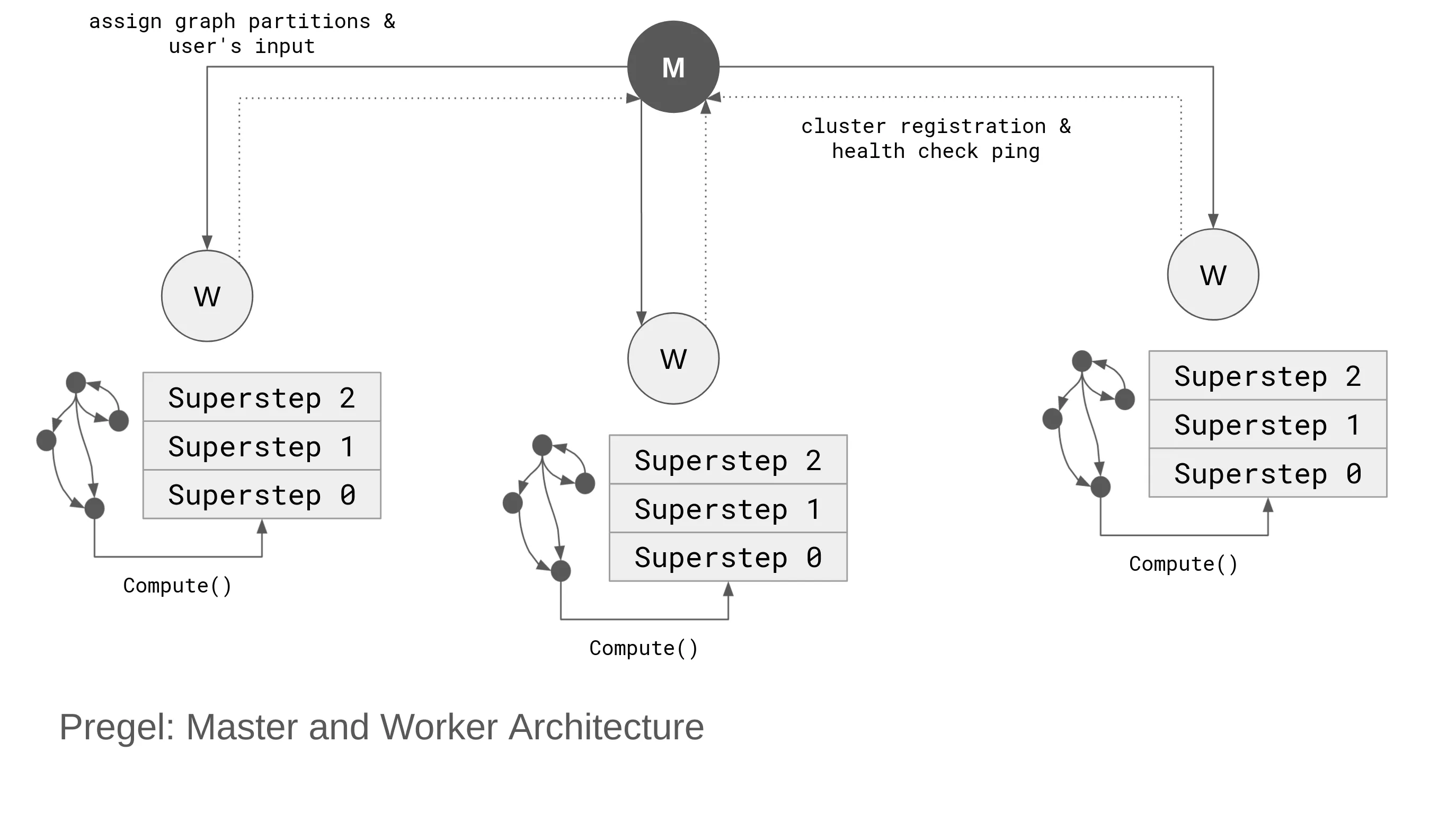
- The master does not handle graph processing directly; it only manages worker states.
- Each worker sends a registration message to the master.
- The master determines how graph partitions are distributed among workers.
- The master instructs workers on executing Supersteps.
Fault Tolerance
Workers continuously send ping messages to the master. If a worker fails to send pings, the master assumes a hardware or network failure and reassigns its partitions to other workers.
To prevent unnecessary recomputation, a checkpoint mechanism is used to track the last successfully executed step, allowing processing to resume from the last valid state rather than starting over.
Worker Implementation
Each worker maintains a HashMap using vertex IDs as keys, storing a set of stateful data, including:
- Current value: The current computed value.
- Outgoing edges: IDs of connected edges.
- Message queue: Messages received from neighboring vertices.
- Vote to halt flag: Indicates if the vertex has completed processing.
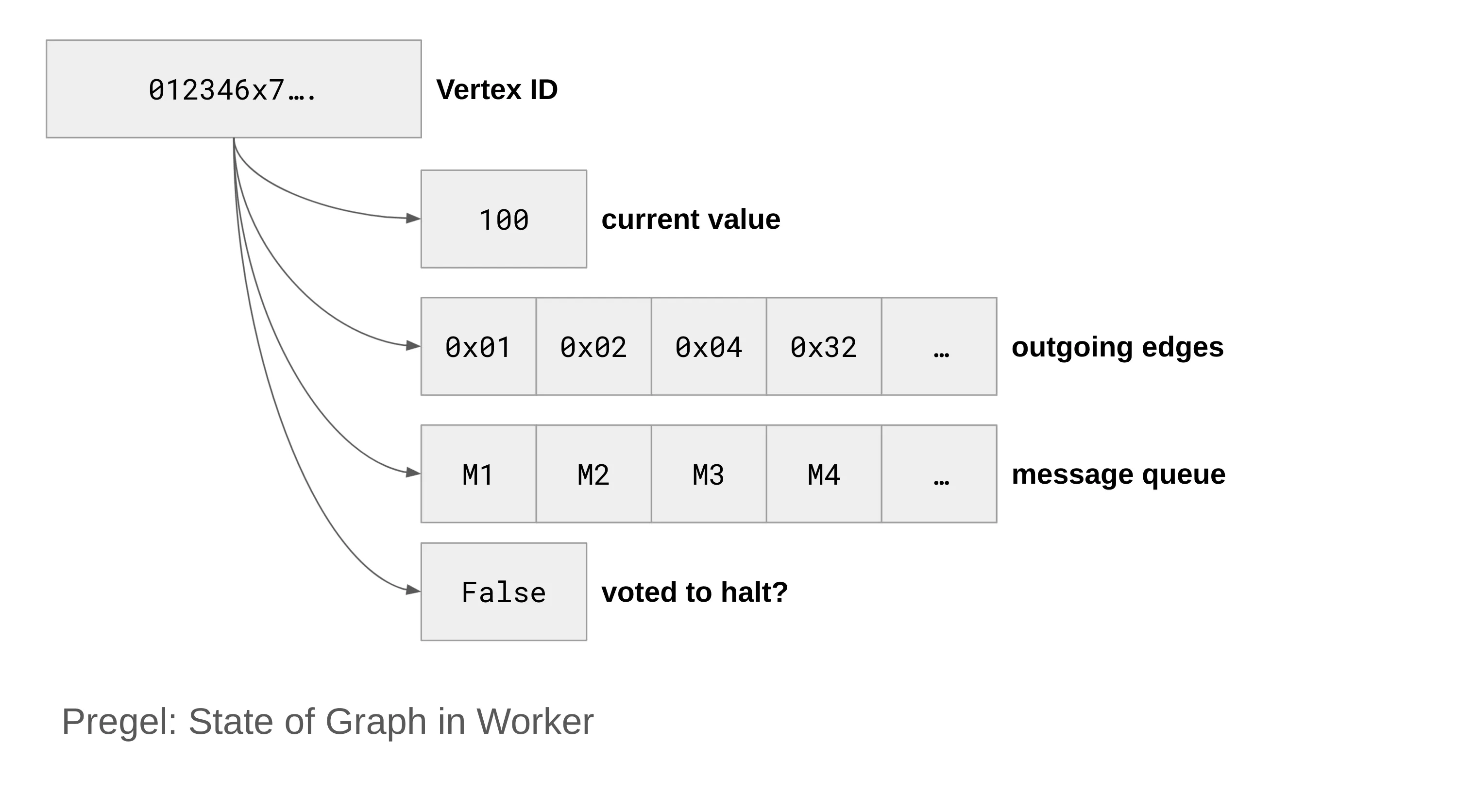
"A worker machine maintains the state of its portion of the graph in memory. Conceptually, this can be thought of as a map from vertex ID to the state of each vertex. The state consists of its current value, a list of outgoing edges (edge targets and current values), a queue of incoming messages, and a flag specifying whether the vertex is active."
Conclusion
This article introduced Pregel, a distributed graph processing engine developed at Google.
Open-source implementations of Pregel include Apache Giraph and Project Pegasus. In the future, I plan to cover these software projects in more detail.